
Researchers have introduced a fully mechanically-free display technology. Unlike conventional flexible displays, which rely on mechanical components such as hinges or sliders to enable shape changes, this new technology achieves shape control without any mechanical parts at all.
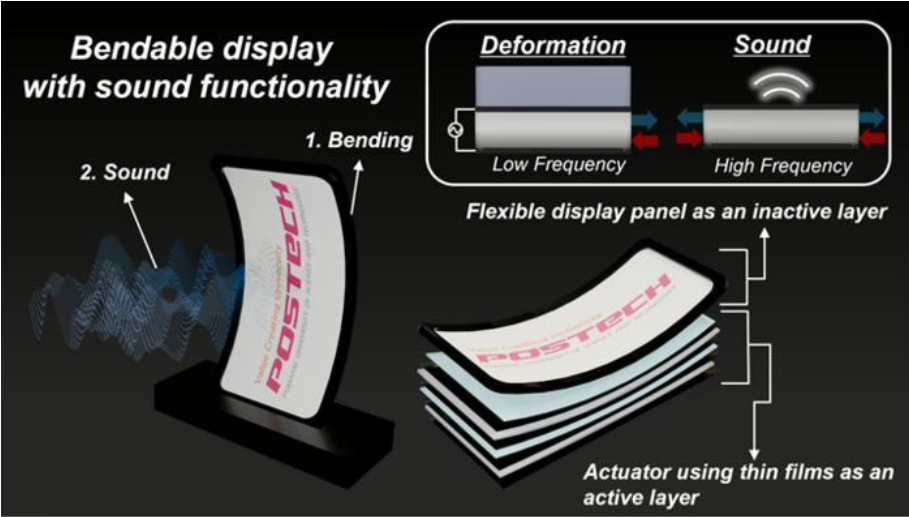
At the core is OLED technology. OLED displays are composed of thin layers of organic compounds situated between two conductive layers, typically a transparent anode and a metallic cathode. When an electrical current passes through these organic layers, they emit light, thus creating images without the need for an external backlight. Because OLED displays generate their own illumination, they can be constructed much thinner and lighter compared to traditional LCD screens, which require backlighting.
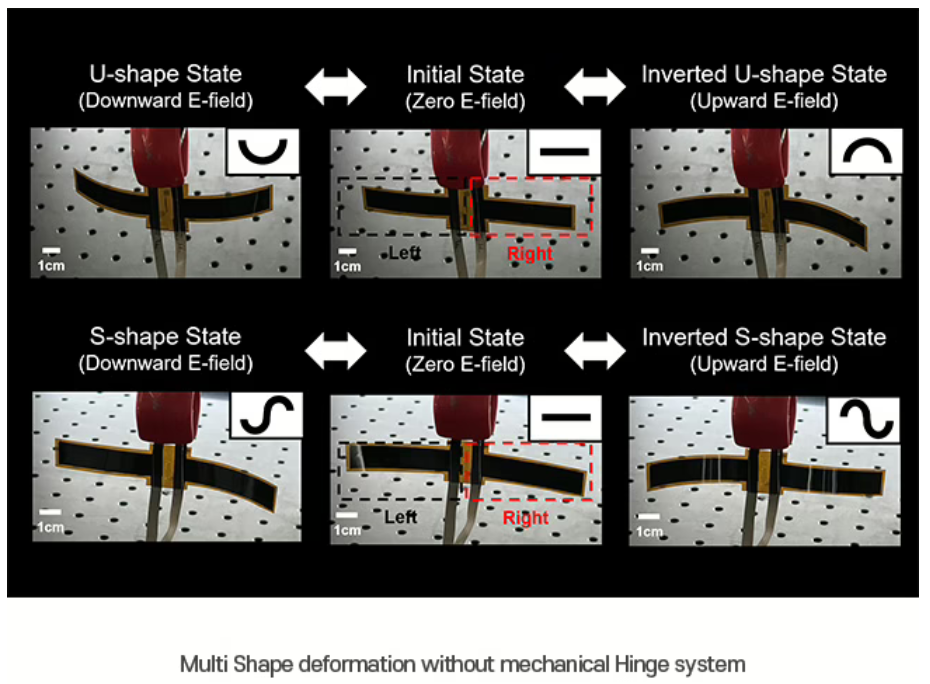
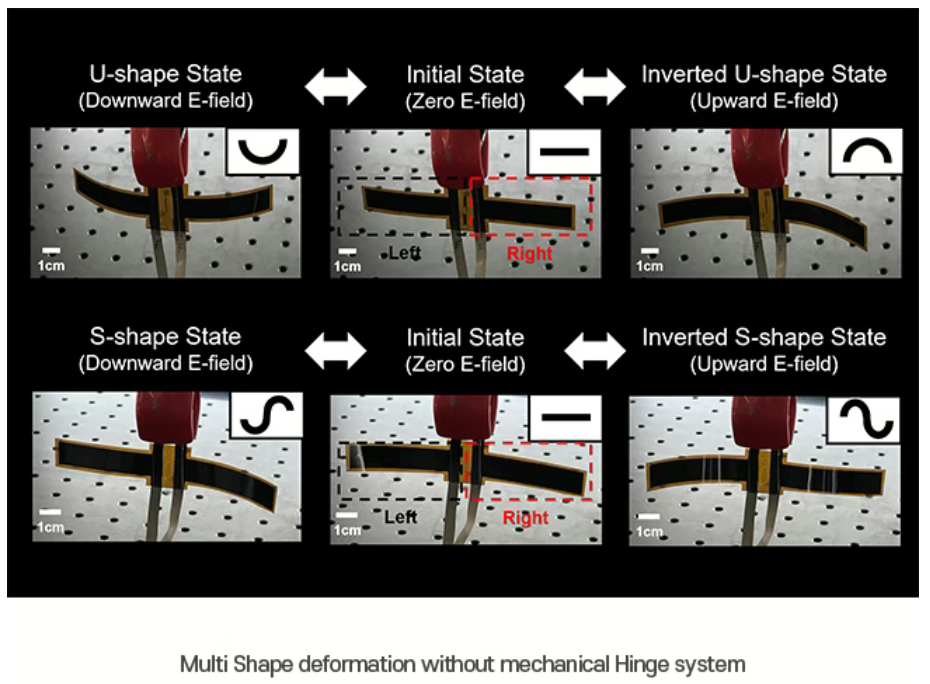
The absence of mechanical components emphasizes OLED’s intrinsic advantages, allowing the display panel to flex, bend, and adopt various shapes more freely. The researchers have specifically demonstrated this capability on smartphone-scale panels, showcasing displays that can dynamically and reversibly transform into different shapes. The reversible aspect is particularly important because it means the panel can continuously change forms without degradation or damage. Such shape adaptability is made possible because OLED’s organic materials and conductive layers can tolerate considerable mechanical deformation without compromising their functionality.
One aspect of OLED’s flexibility is that the materials involved, including the organic emissive layers and electrodes, can maintain their electrical and optical performance even when repeatedly bent or curved. By removing mechanical elements completely, researchers have reduced overall device weight and complexity.
The demonstrations of this new mechanically-free technology specifically targeted smartphone-sized screens. This represents the most common form factor in consumer electronics. Smartphones require durable yet flexible screens capable of repeated shape transformations.
Beyond smartphones, researchers suggest substantial opportunities for broader applications. In the automotive industry, this flexibility could enable displays to fit seamlessly into the contours of vehicle interiors. Automotive displays often face constraints due to rigid flat panels, but flexible OLED screens can conform to dashboards or other interior surfaces without compromising image quality or usability.
The technology also holds promise for soft robotic interfaces, an emerging field where flexible and adaptive materials are crucial. Soft robots, which interact safely and effectively with human users, could integrate these mechanically-free OLED screens into their bodies or limbs, enhancing their ability to visually communicate or dynamically adjust their physical forms in response to environmental interactions or user needs.
Name: lily
Mobile:8613684959210
Tel:0755-27325331
Whatsapp:8618573329919
Email:sales12@huayuan-lcd.com
Add:Factory No.9, Zhongnan High-tech Intelligent Manufacturing Industrial Park, Tianyuan District, Zhuzhou,Hunan, China, 412000